Following is the example of "Shallow copy".
class A;
int var_i;
function new();
$display("Class A is created.");
endfunction
function void
display(string inst_name = "");
$display
("%0s:: Value of var_i=%0d", inst_name, var_i);
endfunction
endclass // class A
class B;
int var_j;
A a_inst;
function new();
$display("Class B is created.");
a_inst = new();
endfunction
function void
display(string inst_name = "");
$display
("%0s:: Value of var_j=%0d", inst_name, var_j);
endfunction
endclass // class B
module top();
initial begin
B b_inst1, b_inst2;
b_inst1 = new();
b_inst1.var_j = 10;
b_inst1.a_inst.var_i = 20;
b_inst2 = new b_inst1;
b_inst1.display("b_inst1");
b_inst1.a_inst.display("b_inst1.a_inst");
b_inst2.display("b_inst2");
b_inst2.a_inst.display("b_inst2.a_inst");
b_inst1.var_j = 30;
b_inst1.a_inst.var_i = 40;
$display
("Value of b_inst1.var_j changed to 30.");
$display
("Value of b_inst1.a_inst.var_i changed to 40.");
b_inst1.display("b_inst1");
b_inst1.a_inst.display("b_inst1.a_inst");
b_inst2.display("b_inst2");
b_inst2.a_inst.display("b_inst2.a_inst");
end
endmodule
Following is the result of the above simulation:
b_inst1:: Value of var_j=10
b_inst1.a_inst:: Value of var_i=20
b_inst2:: Value of var_j=10
b_inst2.a_inst:: Value of var_i=20
Value of b_inst1.var_j changed to 30.
Value of b_inst1.a_inst.var_i changed to 40.
b_inst1:: Value of var_j=30
b_inst1.a_inst:: Value of var_i=40
b_inst2:: Value of var_j=10
b_inst2.a_inst:: Value of var_i=40
b_inst1:: Value of var_j=10
b_inst1.a_inst:: Value of var_i=20
b_inst2:: Value of var_j=10
b_inst2.a_inst:: Value of var_i=20
Value of b_inst1.var_j changed to 30.
Value of b_inst1.a_inst.var_i changed to 40.
b_inst1:: Value of var_j=30
b_inst1.a_inst:: Value of var_i=40
b_inst2:: Value of var_j=10
b_inst2.a_inst:: Value of var_i=40
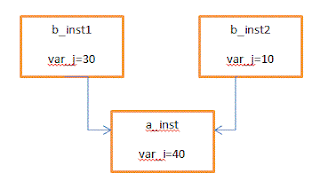
In the above code, statement "b_inst2 = new b_inst1", creates a shallow copy for instance "b_inst2". That means, creating a new object "b_inst2" whose class properties are copied from the object "b_inst1". All the class variables and instance handles are copied from "b_inst1" to "b_inst2". However, the instance handles within "b_inst1" and "b_inst2" points to the same object as shown in the below image, though new() is written for that instance handles.
I hope this post helped to understand shallow copy. Please provide feedback/suggestions in the comment section.
No comments:
Post a Comment